Consider your work experience from last week. Have you checked your email using Google Mail? Do you collaborate with your team via Slack or Microsoft Teams?
Have you managed a task through Asana and Trello? Have you updated your list of clients on Salesforce? Perhaps you can unwind by watching the latest movie streaming on Netflix?
If you said yes to one of the above questions answers then youre an active and every day customer of Software as a Service (SaaS). A few years ago purchasing the latest software to run your business was a huge project.
This involved the purchase of costly physical copies (like CD ROMs) as well as purchasing a small number of “seat licenses” and the hiring of a dedicated IT department to manage and install software on personal computer systems and large in house servers.
Updates required manual effort and compatibility was an ongoing issue and the huge price upfront was an obstacle for anyone wanting to get into the market. Software as a Service (SaaS) completely re invented the model. Software was turned from an actual item you purchase into the service you can subscribe to.
Instead of installing a program on your drive instead it is now accessible on the internet hosted by a services robust cloud servers. The service provider the SaaS businesshandles everything related to maintenance upgrades the security as well as the infrastructure. It is easy to sign up using an internet browser or easy app and youre ready to go working.
This cloud delivery model has become the dominant force in the modern tech economy creating a multi hundred billion dollar industry. This has evened out the playing field and allowed startups of all sizes to access the same high end enterprise grade technology that an Fortune 500 company for a affordable monthly price.
This is the comprehensive reliable resource for the subject of SaaS. The topics we will discuss include:
- What is SaaS refers to and how its fundamental structure works.
- There is a clear distinction in SaaS PaaS IaaS SaaS and IaaS.
- The significant positives (and crucial issues) of using the SaaS model.
- What is the method by which SaaS businesses earn money is with a range of pricing strategies and business strategies.
- The most important indicators to measure success within the SaaS world (MRR Churn LTV).
- Future of SaaS Future of SaaS includes AI integration vertical markets Micro SaaS.
If youre a leader in the business who is deciding to use a brand new software or an IT professional who is managing an IT stack or business owner who has an SaaS concept this article can provide you with the complete knowledge you require.
The Core Concept: How Does SaaS Actually Work?
The simplest way to describe it is that SaaS is an example of a service that is delivered via software that a third party provider creates the application and makes it accessible to users via the internet.
What happens “under the hood” is the true magic. Cloud delivery concepts and multi tenancy is what makes the complete SaaS model feasible and economical.
The Cloud Delivery Model Explained
Consider traditional in house software as driving the car. The responsibility lies with you for all of it starting with the purchase (a expensive Capital Expensive also known as Capital Expenditure) as well as the insurance policy and fuel costs maintenance (oil change and tires rotations) as well as finding an appropriate place to park the vehicle. When it fails you are the one to address the issue.
SaaS On contrary is the same as the use of the ride sharing platform similar to Uber and Lyft.
- Its not your car.
- The cost is a tiny regular fee per journey (a OpEx which is also referred to as Operating Cost).
- The company handles the car its driver maintenance insurance as well as the fuel.
- The service is used to travel to Point A to Point B at any time and on demand.
The SaaS service provider (like Google Microsoft or Salesforce) is responsible for the software as well as the data that runs it and servers as well as the network infrastructure and important security patches as well as software update.
The user can just need to connect to this completed and ready to use service. The online software solution eliminates the hassle of maintenance and ownership.
The Key to SaaS: Multi Tenant Architecture
This is the most crucial technological concept that you need to comprehend. Most SaaS applications run using the basis of a multi tenant structure. Consider an apartment.
- Its an one of a kind design (the infrastructure) developed by a software developer (the SaaS provider).
- It accommodates numerous customers (customers) all at the at the same time.
- Every tenant is assigned their individual private apartment (their information configurations and the user accounts).
- All are part of the same resource such as electricity plumbing as well as security (the underpinning code databases and server power).
It is extremely effective. The service provider is responsible for only one only one common application and database. If they release an update or bug solution every customer receives it immediately.
The sharing of resources is the reason that is what makes SaaS such a low cost and affordable. Every tenants personal information is distinct and hidden from other tenants providing confidentiality and security in the shared space.
Single Tenant or. Multi Tenant: Whats The difference?
Although multi tenancy is the norm but some SaaS service providers also have the single tenant type of service usually as an option that is ideal for enterprises with extremely secure or requirements for customization.
- Multi Tenant (The Apartment Building): One software instance can be shared among many clients.
- Benefits: Lower cost (due to sharing resources) Instant updates for all users excellent capacity and less hassle for users.
- Con: Less customization (you arent able to “remodel” the buildings plumbing) and shared assets (a “noisy neighbor” could possibly affect performance but its not common).
- Single Tenant (The Townhouse or Detached House): Each customer receives their very own version of the program and the database.
- Advantages: High customization (you are able to “remodel” your own home) and complete data isolation greater control over updates and the environment.
- Con: Extremely expensive (youre paying for your entire house instead of just one unit) slow update (must be applied to every instance) the customer is the one to pay for upkeep.
In the majority of companies that are in the majority a multi tenant system is the best combination of cost power and ease of use.

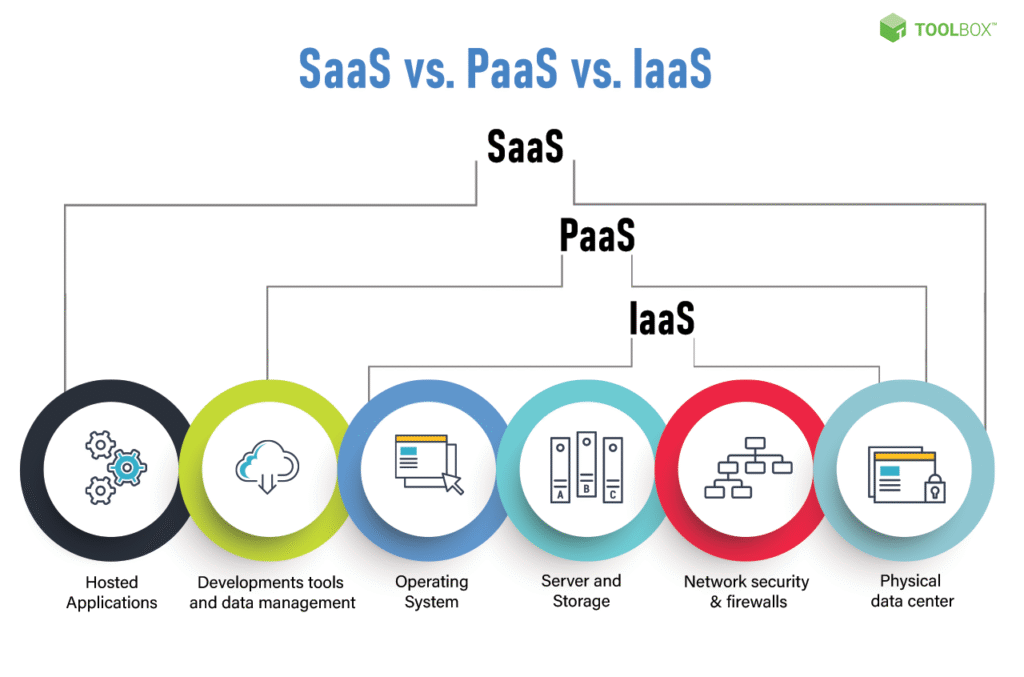
The Big Three: SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS explained
SaaS is one of three major categories in cloud computing. Theres a good chance youll see it mentioned in conjunction with PaaS as well as IaaS. Knowing the distinction is essential to know what youre purchasing.
The three models that are discussed hereinafter are referred to by the name of “cloud computing stack.” The most straightforward way to grasp it is through the well known “Pizza as a Service” analogy.
The Cloud Computing Stack: A Quick Overview
Imagine having a an event with pizza. There are four choices:
- on premise (The “Make at Home” Model): You do all the things. You purchase the ingredients: tomatoes flour as well as cheese. You own your oven electric a power source and a pizza peel. Make the pizza dough then cook the pizza and serve it up on your personal plates. Its like the typical off premise software.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as an service): You rent the kitchen. The oven is not yours to own as well as the stove or the structure however you are accountable for the dough along with sauce as well as toppings and cook your pizza on your own.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): You order pizza delivery. The Kitchen (the platform) prepares your pizza and you make the request (the software) and are accountable in setting up the table and serving the pizza.
- SaaS (Software as an service): You go to a place of dining. Then you sit down and take a seat and order. Restaurant staff handle all the detailsthe ingredients cooking as well as the service and the cleaning. It is your responsibility to consume the food.
This is a clear definition of”the “separation of concerns”it boils down to who controls what.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): The Foundation
IaaS is the simplest element of cloud. When you use IaaS youre basically renting the IT infrastructure that is essential to your business.
- What is it: You rent virtual servers storage and networking equipment through a supplier. It comes with “hardware” (though its virtualized) and you can create whatever youd like over it.
- You are in charge of: The applications the runtime data middleware as well as the operating system.
- Provider manages: The servers networks storage as well as the virtualization layer.
- An analogy: Leasing the land and a kitchen that is empty. The cookware you bring is your own along with the ingredients and your staff.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS) Microsoft Azure Google Compute Engine (GCE).
- Who is it for? System administrators network architects and IT departments that require the most control of their infrastructure.

PaaS (Platform as a Service): The Workshop
PaaS is a service that allows developers to create tests deploy and test applications without having to worry about the infrastructure.
- What is it: The provider manages operating systems servers and databases. The user is provided with an “sandbox” or “workshop” that allows you to concentrate on creating the code for your application.
- You are in charge of: Your applications and information.
- Provider manages: Everything in IaaS plus the runtime middleware as well as the operating system.
- Analogous to: Renting a fully fitted kitchen. The stove oven and counters come with. All you need to bring is your food along with your the recipe.
- Examples: Heroku Google App Engine AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
- Who are the users? Software developers and team members working on application development.
SaaS (Software as a Service): The Finished Product
SaaS is the most comprehensive and popular cloud based service that delivers an application that is ready to use for the user.
- What is it: It is a fully functional completed software application you can connect to using your browser. There is no management building or install or deploy anything. Its just used.
- You Manage: Nothing. (Well you manage your personal preferences and user information However the software the software).
- Provider Manages: Everything. Everything starting from servers all the way to the application.
- An analogy: ordering a pizza delivery right to your doorstep or eating at an eatery. Its just food.
- Examples: Salesforce Gmail Slack HubSpot Zoom.
- Who are the users? End users like representatives from sales teams marketing teams HR specialists as well as nearly every employee.
Comparison Table: Who Manages What?
Below is a quick description of how you can manage in comparison to what the cloud service provider is managing in each the model.
| Management Layer | On Premise | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Applications | You Manage | You Manage | You Manage | Vendor Manages |
| Data | You Manage | You Manage | You Manage | Vendor Manages |
| Runtime | You Manage | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Middleware | You Manage | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Operating System | You Manage | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Virtualization | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Servers | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Storage | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
| Networking | You Manage | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages | Vendor Manages |
The Undeniable Benefits: Why Businesses are Moving to SaaS
The rapid growth of SaaS is not an accident. The model provides powerful and tangible benefits for businesses in all sizes ranging whether a single person business or large scale enterprises.
1. Financial Advantage: From CapEx to OpEx
It is by far the biggest profit in terms of money.
- traditional software (CapEx): You have to deal with a huge capital expenditure (CapEx). It is necessary to purchase servers buy expensive perpetual licenses as well as spend money on installations and training before you know whether its a good choice for you.
- SaaS (OpEx): You are able to predict your Operating Cost (OpEx). Its a cost effective annually or monthly subscription. This allows cash flow to be free and makes budgeting easy and drastically reduces total cost of ownership (TCO). It is not a surprise to pay cost for maintenance or upgrades.
2. Accessibility and Mobility
SaaS applications were “born” on the internet. It means that you are able to access your data tools and work with your team any time anywhere from any device (computer smartphone tablet or smartphone) provided you are connected to the internet. This is the key element of modern remote working as well as the the global group revolution.
3. Painless Automatic Updates
On premise software “patch Tuesday” was a unwelcome day. The updates were time consuming manual and frequently broke the other system. When you use SaaS providers they handle every aspect of changes.
It is always updated with the most recent version the most secure and the most advanced version of the program. Security patches are distributed centrally and quickly. Updates are distributed to everyone automatically with no downtime nor time by your IT staff.
4. Rapid Deployment and Scalability
- deployment: Instead of a long term installation plan You can roll out an entirely new SaaS tool within minutes. Simply sign up make an account and invite your entire team.
- Scalability Its a major benefit. When you add 100 new workers and you want to expand your business there is no have to purchase 100 additional servers. Just visit your subscription settings and click “add 100 users.” The flexibility can be reversed as well. In the event that you have to cut down on your usage it is possible to quickly reduce your subscription making only the charges youre using.
5. Reduced IT Burden
In the world of on premise IT staffs typically spend their time “keeping their lighting on”managing servers re updating software and repairing Issues with compatibility. There are compatibility issues.
SaaS model removes the IT department from these mundane tasks. Instead of securing servers. Theyre able to concentrate on strategic high value projects that propel your business to the next level including optimizing business processes or developing custom integrations.
- What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) | Master Guide 2026
- Agentic AI and Autonomous Agents: Guide to the Next Evolution of Ai
- Options Trading Automation Using Python: Complete Beginner Guide
- Synthetic Data Generation: The Ultimate Master Guide 2026
- GitHub Copilot Master Guide 2026: The Ultimate AI Coding Handbook